All you need to know about papillary thyroid cancer
Papillary thyroid cancer, also known as papillary carcinoma, is the most common type of thyroid cancer. Over 75 to 85% of all incidences of thyroid cancer is papillary thyroid cancer. It is three times more common in women as compared to men. Exposure to radiation is known to be the main cause of this illness. This type of thyroid cancer can occur at any age from childhood to old age, but it mostly affects people in the age group of 30 and 50 years.
Here are some must-know facts on papillary thyroid cancer:
1. Prevalence
Thyroid cancer is the fifth-most common malignancy in women in the country. With the increasing number of this cancer being recorded, there have been efforts to spread awareness about it. Any suspicious symptoms and growth and changes in thyroid glands have to be screened. With immediate medical attention and correct treatment, papillary thyroid cancer has a high cure rate. About 90% survive for more than 10 years after treatment.
2. Symptoms and diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer
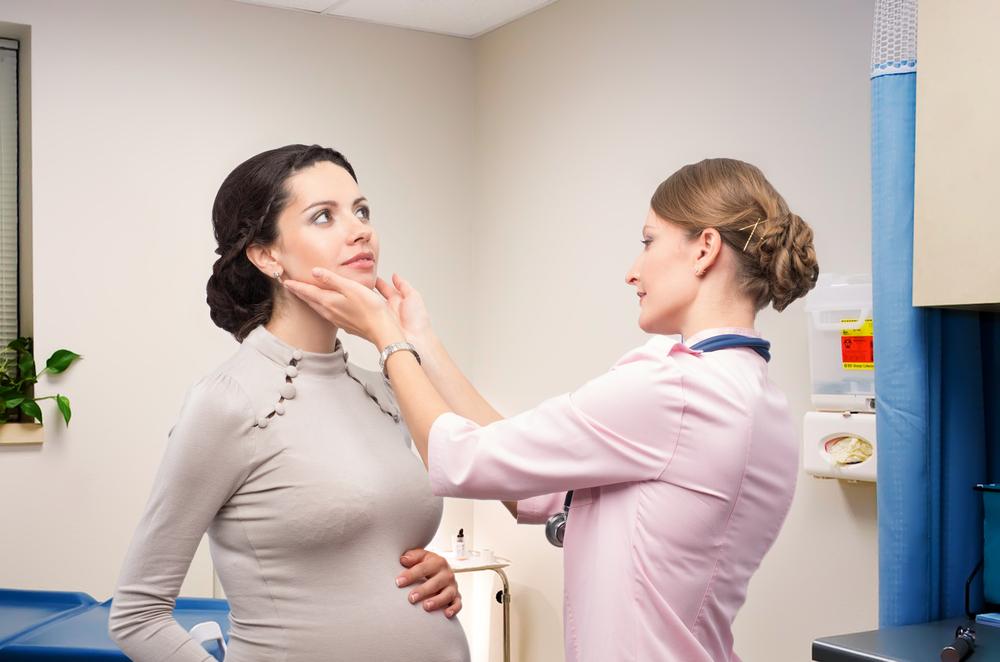
It can be surprising to note that papillary carcinoma usually has no symptoms, and it rarely causes hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. The main symptom is a swelling or a lump in the throat. This is normally noted by the patient themselves or by a doctor during an examination of the thyroid gland or throat. The doctor checks for swelling or lumps in the throat. Any suspicion is confirmed with a scan or X-ray. A needle biopsy is recommended to identify any worrisome lumps or nodules. Without any symptoms until much later, there is invariably a delay in diagnosis. By then cancer in most patients would have reached advanced stages.
3. Stages of papillary carcinoma and treatment
The grading or staging of this type of cancer differs from the staging of other types of cancer. It depends on the age of the patient, the size of the tumor, and the spread of cancer to the lymph nodes and other areas. Staging is done to determine the intensity of the surgery, as surgery is the primary treatment for thyroid cancer. Staging is also done to determine the type of treatment. It is done if the cancer is:
- Big (larger than 1.0 centimeter) – Thyroidectomy is conducted, which is a procedure that removes the thyroid glands.
- Small (smaller than 1.0 centimeter) – Lobectomy is done to remove the lobe on the malignant side of the thyroid.
In about 50% of the cases, if the cancer spreads to the neck, then the removal of thyroid and lymph nodes is done to prevent the cancer from spreading further. Thyroidectomy patients are started on thyroid replacement therapy immediately after the procedure is completed.
4. Thyroid cancer and vocal cords
Thyroid tumors can sometimes affect the function of your voice box (vocal cords). A minor procedure called laryngoscopy is done by the doctor to view the larynx. It is better to do this procedure to confirm normalcy of the larynx, as sometimes even if your voice sounds normal the vocal cords may not be functioning properly.
5. Post-surgery and recovery
Schedules and periodic visits to the doctor are necessary to monitor if there is any recurrence of the malignancy. Certain blood tests are done regularly to ensure that the cancer is cured, and to detect any recurrence at the earliest stage.