Different Types of Meningitis
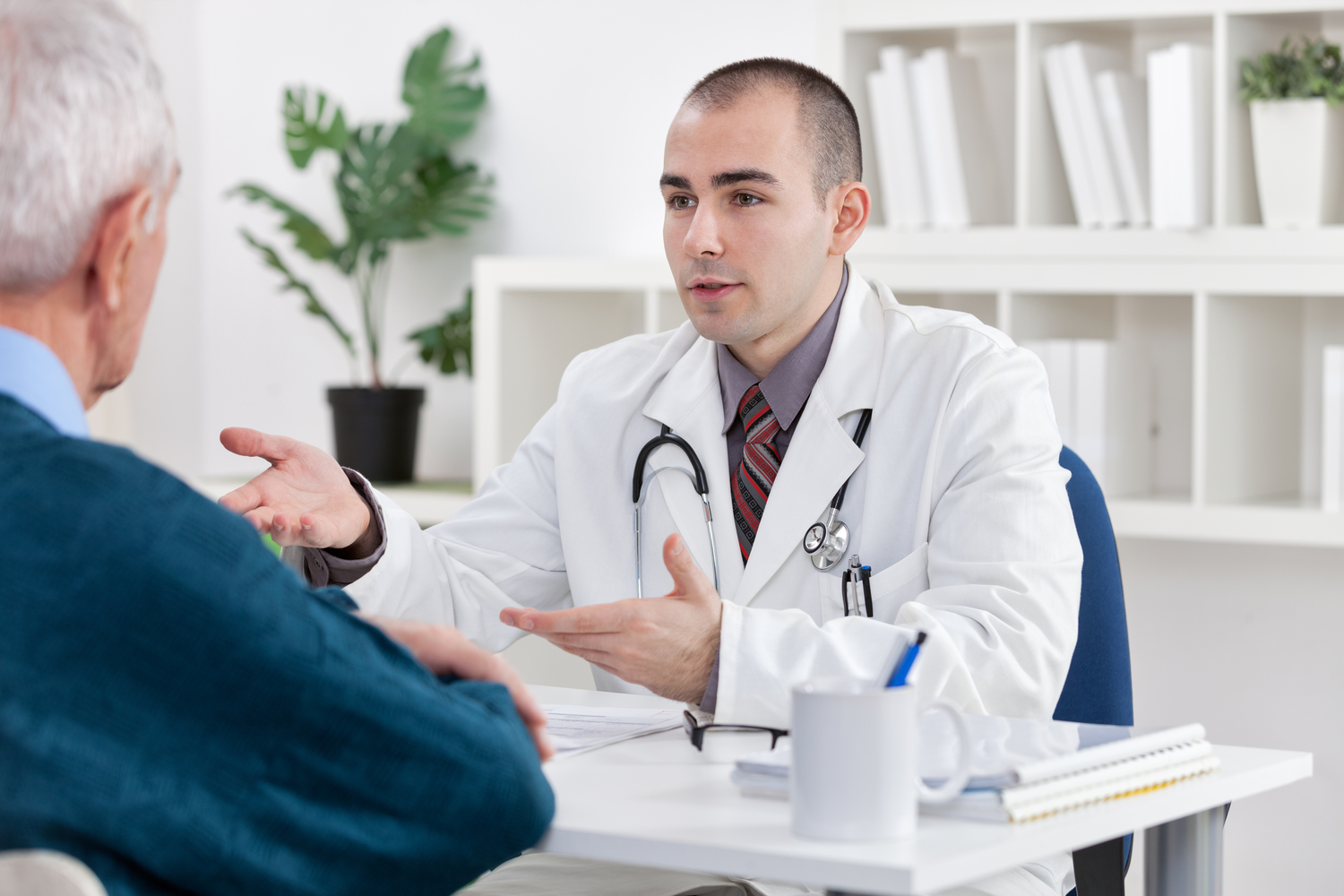
Meningitis refers to the inflammation of the brain membranes and those surrounding the spinal cord. The membranes are called meninges. When meninges swell, they trigger some flu-like symptoms. Some of the symptoms include headache, stiff neck, and fever, coughing, and vomiting. Meningitis can be caused by a viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infection. Weak immune system is one of the biggest meningitis risks. The good news about it is that it is treatable during the early stages, but when it complicates, it can be life-threatening.
There are five types of meningitis and they are as follows:
1. Bacterial meningitis
As the name suggests, this type of meningitis is caused by bacteria. How? When bacteria enter the bloodstream and get to travel to the brain cells or the spinal cord. This is an indirect way of getting meningitis but you can get it when bacteria invade the brain membranes directly. How will the bacteria get to your brain or spinal cord? When you get a sinus or ear infection, when you have a skull fracture and some surgeries might expose you to the bacteria. Some of the bacteria causing meningitis include streptococcus pneumonia ( also causes pneumonia), Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae, and Listeria monocytogenes. Its symptoms include fever, headache, rashes, vomiting, confusion, flu. As soon as you experience the symptoms see your doctor for treatment. Bacterial Meningitis can be treated with antibiotics.
2. Viral meningitis
This type of meningitis is caused by a group of viruses called enteroviruses. In the United States, the viruses are common in early fall and late summer. Some viruses that can cause viral meningitis are HIV, West Nile, herpes simplex virus and mumps. Its symptoms are similar to those of bacterial meningitis. The viruses do not grow in the cerebrospinal as bacteria do, but they resolve on their own. Therefore, there is no specific treatment for viral meningitis, though you can treat it with antiviral medication. It can be spread via fecal contamination and poor hygienic practices is among meningitis risks. For prevention, ensure that you are vaccinated against measles, chickenpox, and mumps.
3. Fungal meningitis
This is another form of meningitis that occurs when the fungus invades your bloodstream. Anyone is at risk of getting this type of meningitis but the one whose immunity is weaker, they are at greater risk. You can get fungal meningitis by inhaling fungal spores from bat droppings, birds, or contaminated soil. Fungal Meningitis can be treated with antifungal medication during the early stages before it advances into complications. The length of treatment depends on the immunity of the patient and the type of fungus.
4. Parasitic meningitis
Parasitic meningitis is caused by a parasite known as Naegleria fowleri. This parasite causes one of the most fatal types of meningitis known as PAM that progresses between one to twelve days. Its symptoms start as those of flu but gradually they progress to confusion, seizures, loss of balance and hallucinations. The parasite is found in lakes, fresh water sources, untreated swimming pools and discharges from industries.
5. Chronic meningitis
This type is caused by slow–growing organisms such as mycobacterium tuberculosis. The organisms invade the brain membranes and brain fluid. It can develop in two weeks after the brain has been invaded. Some of its symptoms include fever, headaches, mental cloudiness, and vomiting. The disease is treatable during the early stages.