Understanding the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes
The diagnosis and treatment of diabetes have to happen instantaneously and not wait till the blood sugar levels go beyond a manageable level resulting in other health complications. So where do you have to start if you need to know if you have diabetes? If you have any hereditary risk factors for diabetes or there are high levels of blood sugar detected in your urine, you would be asked by your medical practitioner to get diagnostics done for confirmation.
Blood glucose, which is the blood sugar level, tends to be high if the insulin production in the pancreas is less or nil. This form of diabetes is categorized as Type 1. However, if the body itself is not responding normally to insulin then it is categorized as Type 2 diabetes.
1. Diagnosing type 1 and type 2 diabetes
The diagnosis for diabetes is done through three types of tests. Most often doctors ask the individuals to get a repeat test or all three tests done to confirm the diagnosis. These three main tests for diabetes diagnosis and treatment include:
- Fasting glucose test: This is a test that helps identify the blood sugar levels early in the morning before the consumption of food. A level that is 126mg/dL or higher is considered as confirmed for diabetes.
- OGTT: This is commonly known as the oral glucose tolerance test. It is a test where an individual is given a beverage containing glucose to drink, and then having the blood sugar levels monitored for about three hours every 30-60 minutes. If the glucose levels increase to 200mg/dL or higher within two hours, then there is a chance the individual has diabetes.
- A1C test: This is a blood test that can help analyze the blood sugar level patterns in an individual for over two to three months. In this test, if the A1C level is 6.5% or higher, then the individual is diagnosed as diabetic.
- Zinc transporter 8 autoantibody test
Another test that a doctor may choose to prescribe is known as the zinc transporter 8 autoantibody (ZnT8Ab) test. This is a form of blood test wherein other factors are tested to determine whether the individual tests positive for Type 1 diabetes over any other type of diabetes. The main objective of this test is to get an accurate diabetes diagnosis and treatment started immediately so that any further possible health complications are averted swiftly.
2. Treating diabetes
Once the diagnosis of diabetes is done, the next stage is treatment. Both diabetes diagnosis and treatment cannot be done by the individuals themselves as this is a quite tricky disease. Creating a treatment plan along with your doctor is essential as they will not only prescribe medication but also guide you in choosing the right set of habits. You need to incorporate some good habits into your lifestyle to keep your diabetes in check. Diabetes requires periodic close monitoring to ensure that you are not allowing any other external factors to aggravate your blood sugar levels or even allow them to drop below the normal requirement.
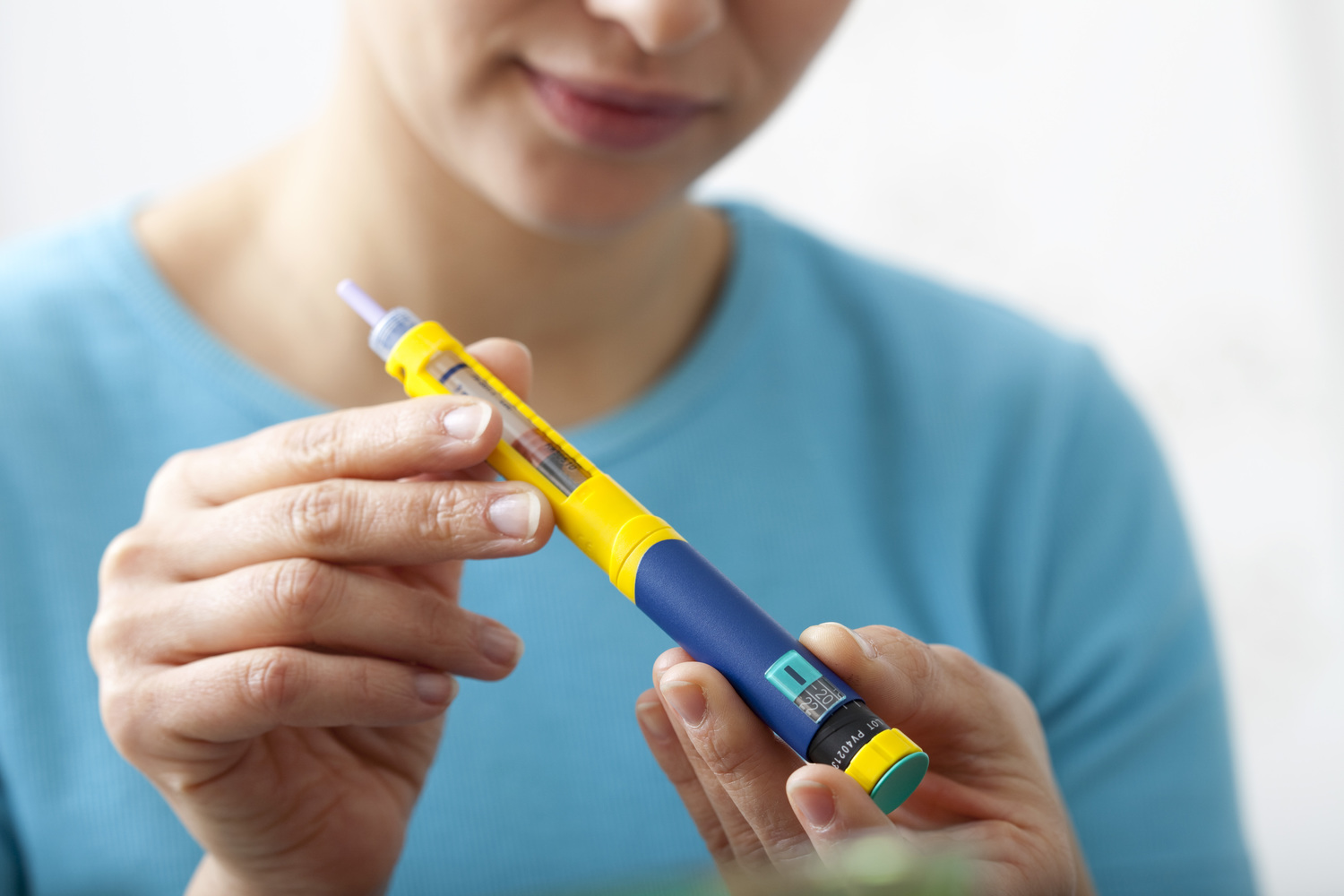
- Treating type 1 diabetes: Most often managed with insulin as well as dietary changes and exercise.
- Treatment for type 2 diabetes: Although type 2 may be managed with non-insulin medications, insulin is commonly prescribed as well as weight reduction via exercise and dietary changes.